What do centrosomes do?
Here is the article in HTML format:
Summary of the Article
The centrosome is an important organelle in cell division and the maintenance of cell shape. It serves as the dominant microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) in animal cells. Centrosomes play a crucial role in organizing microtubules, determining cell shape and polarity, and organizing the mitotic spindle during the cell cycle. Without centrosomes, chromosomes serve as the primary organizer of the bipolar spindle. However, if centrosomes are present, they become the primary organizer of the spindle. Centrosomes are membrane-free organelles found in different eukaryotic lineages and are involved in cell polarity, cell division, and development in most animal species. Centrosomes help maintain the chromosome number during cell division and stimulate changes in cell membrane shape through phagocytosis. They are essential for correct cell division and the distribution of centrioles in daughter cells. If there were no centrosomes, cell division would still occur, but the spindle organization would rely solely on chromosomes. Microtubules are made in the centrosomes, and during mitosis, the centrosome divides and moves to opposite sides of the dividing cell. The centrioles are critical for the formation of the mitotic spindle, while the centrosome itself is an area of the cell near the nucleus where the centrioles reside when the cell is not undergoing mitosis. The centrosome is the main microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) in animal cells and plays a vital role in cellular function and regulating cell division.
Questions and Detailed Answers
1. What are the two functions of the centrosome?
The centrosomes help in cell division and maintain the chromosome number during cell division. They also stimulate changes in the shape of the cell membrane through phagocytosis. In mitosis, they help organize the microtubules to ensure distribution to each daughter cell.
2. What is the function of the centrosome in the cell cycle?
Centrosomes act as the dominant microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs) in animal cells during the cell cycle. They determine the spatial arrangement of microtubule arrays, influencing cell shape, polarity, motility, and organization of the mitotic spindle.
3. What are important facts about centrosomes?
Centrosomes are membrane-free organelles that serve as the main microtubule-organizing centers in eukaryotic lineages. They play key roles in cell polarity, cell division, and development in most animal species.
4. What is the function of centrosome vs centriole?
Centrioles are critical for the formation of the mitotic spindle and cytokinesis. The centrosome, on the other hand, is the area of the cell where centrioles reside when the cell is not undergoing mitosis.
5. Is the centrosome necessary for mitosis?
In many cells, the centrosome with its centrioles is essential for correct cell division. The centrosome ensures the distribution of the right number of centrioles to each daughter cell.
6. What would happen if there were no centrosomes?
In the absence of centrosomes, chromosomes serve as the primary organizer of the bipolar spindle. However, if centrosomes are present, they become the primary organizer of the spindle. The latter stages of mitosis, anaphase and telophase, can still occur without centrosomes.
7. What is the function of centrosome quizlet?
The centrosome is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides, and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell.
8. What is the difference between centrosome and centrioles?
Centrioles are paired barrel-shaped organelles near the nuclear envelope in animal cells’ cytoplasm. The centromere, on the other hand, is the central region of the chromosome that consists of highly constricted DNA. The centrosome is the organizing center of all microtubules in an animal cell.
9. What is the function of the centrosome quizlet?
The centrosome is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides, and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell.
10. Why is the centrosome important?
The centrosome is the main microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) in animal cells and plays a crucial role in cellular function and regulating cell division.
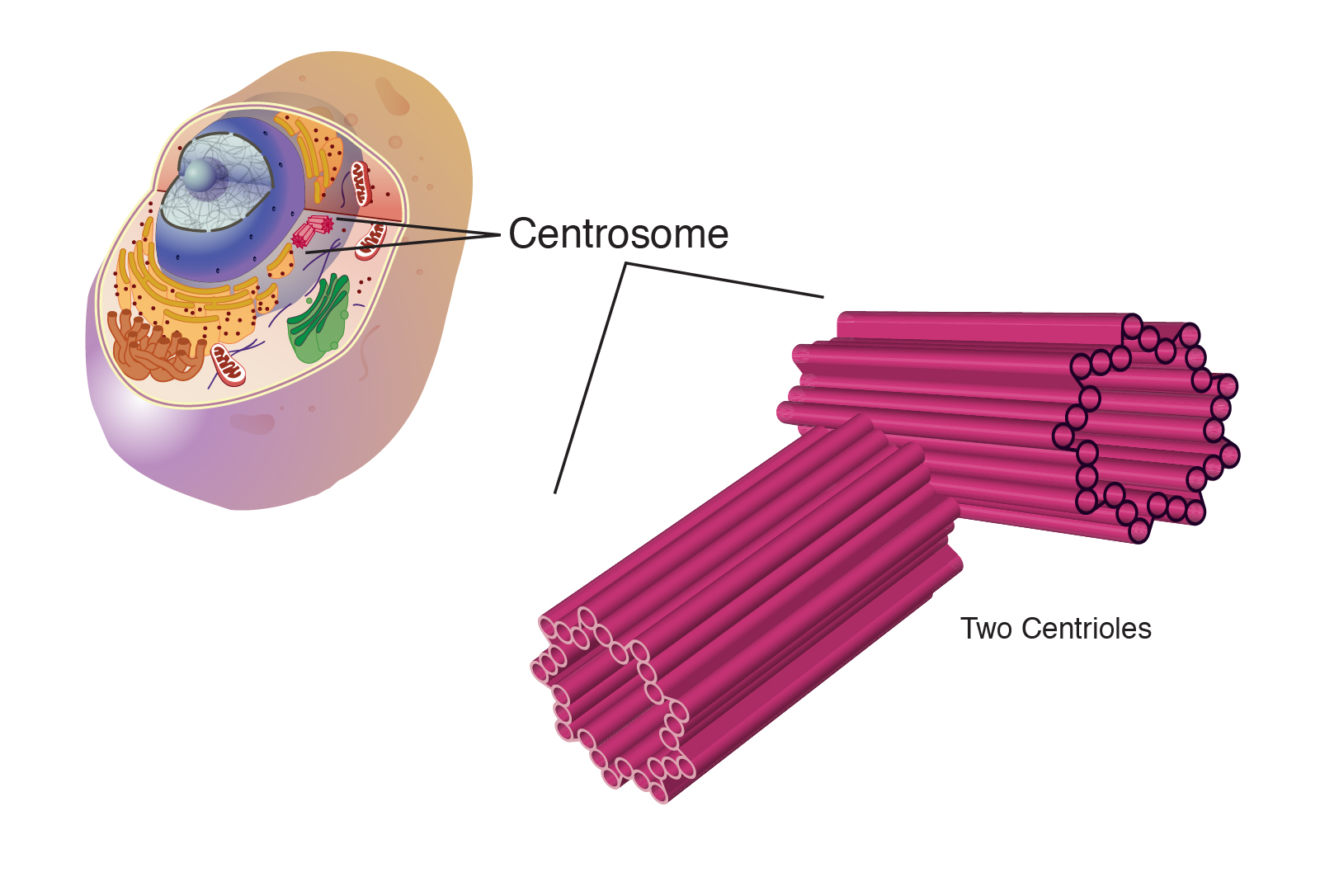

What are the two functions of centrosome
The centrosomes help in cell division. They maintain the chromosome number during cell division. They also stimulate the changes in the shape of the cell membrane by phagocytosis. In mitosis, it helps in organizing the microtubules ensuring that the centrosomes are distributed to each daughter cell.
What is the function of the centrosome in the cell cycle
Centrosomes are cytoplasmic organelles which act as the dominant microtubule-organising centres (MTOCs) in animal cells. During the cell cycle, centrosomes determine spatial arrangement of the microtubule arrays to influence cell shape, polarity, motility and organisation of the mitotic spindle [47,48].
What are important facts about centrosome
Centrosomes are membrane-free organelles that serve as main microtubule-organizing centres in distinct eukaryotic lineages. Through their ability to organize microtubules, they are involved in cell polarity and cell division, and play key roles in the development of most animal species [1,2].
What is the function of centrosome vs centriole
So the centrioles are critical to allow the mitotic spindle to form, which is critical to allow cytokinesis. As to be distinguished from the centrosome, which is an area of the cell next to the nucleus where the centrioles normally live when the cell is not undergoing mitosis.
Is the centrosome necessary for mitosis
So in many cells, the centrosome with its centrioles is indeed essential to ensure correct cell division, and in these the PCM ensures the distribution of the right number of centrioles to each daughter cell.
What would happen if there were no centrosomes
In the absence of centrosomes, chromosomes serve as the primary organizer of the bipolar spindle. However, if centrosomes are present, they become the primary organizer of the spindle. Our results also demonstrate that the latter stages of mitosis, anaphase and telophase, can occur in the absence of centrosomes.
What is the function of centrosome quizlet
The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell.
What is difference between centrosome and centrioles
Centrioles are paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope. The centromere is the central region of the chromosome which consists of highly constricted DNA. The centrosome is an organelle that serves as the organizing centre of all microtubules in an animal cell.
What is the function of the centrosome quizlet
The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell.
Why is centrosome important
The centrosome is the main microtubule organising centre (MTOC) in animal cells and plays an important role in cellular function and regulating cell division.
What happens to a cell without centrosomes
In the absence of centrosomes, chromosomes serve as the primary organizer of the bipolar spindle. However, if centrosomes are present, they become the primary organizer of the spindle. Our results also demonstrate that the latter stages of mitosis, anaphase and telophase, can occur in the absence of centrosomes.
Can a cell divide without a centrosome
Cells are full of organelles — busy little structures that carry out specific jobs within the cell. Some organelles are similar in all multi-celled organisms, but one cell structure that's found almost exclusively in animal cells is the centriole.
What is the role of the centrosome is it necessary for mitosis
The centrosome is present in most animal cells and functions as the major microtubule-organizing center to ensure faithful chromosome segregation during cell division. As cells transition from interphase to mitosis, the duplicated centrosomes separate and move to opposite sides of the cell where the spindle assembles.
What is the main function of centrosome and centrioles
Centrosomes are structures found inside of cells. They are made from two centrioles. Centrioles are microtubule rings. The main purpose of a centrosome is to organize microtubules and provide structure for the cell, as well as work to pull chromatids apart during cell division.
What is the function of the centromere and centrosome
Function. Centrosome: Centrosomes anchor spindle microtubules in order to form the spindle apparatus during the cell division. Centromere: Centromeres hold two sister chromatids together in a replicated chromosome.
What would happen without centrosomes
In the absence of centrosomes, chromosomes serve as the primary organizer of the bipolar spindle. However, if centrosomes are present, they become the primary organizer of the spindle. Our results also demonstrate that the latter stages of mitosis, anaphase and telophase, can occur in the absence of centrosomes.
What is a fact about centrosome
The centrosome is the major microtubule-organizing center in the cell. During interphase the centrosome is responsible for creating a microtubule array and during mitosis it assists in bipolar spindle assembly. Tissue development and homeostasis depend on the polarizing activity of the centrosome.
What happens if the centrosome stops working
Structural and numerical centrosome abnormalities trigger mitotic errors, cellular senescence, cell death, genomic instability and/or aneuploidy, resulting in human disorders such as aging and cancer and affecting immunity.
What will happen if there is no centrosome
In the absence of centrosomes, chromosomes serve as the primary organizer of the bipolar spindle. However, if centrosomes are present, they become the primary organizer of the spindle. Our results also demonstrate that the latter stages of mitosis, anaphase and telophase, can occur in the absence of centrosomes.
Is centrosome necessary for mitosis Why
Centrosomes not only nucleate but also organize microtubules of the mitotic spindle. The mitotic spindle is anchored to the cell cortex by the astral microtubules emanating from the centrosomes. Proper orientation of the mitotic spindle is essential for correct cell division.
What are the facts about centrosomes
Centrosomes are membrane-free organelles that serve as main microtubule-organizing centres in distinct eukaryotic lineages. Through their ability to organize microtubules, they are involved in cell polarity and cell division, and play key roles in the development of most animal species [1,2].
What is one of the main functions of a centromere
The primary function of the centromere is to provide the foundation for assembly of the kinetochore, which is a protein complex essential to proper chromosomal segregation during mitosis.
What is in the centrosome
The centrosome is composed of two barrel-shaped microtubule-based organelles, the centrioles, surrounded by proteins collectively called the pericentriolar material (PCM). Proteins of both the centriole and the PCM can nucleate and anchor microtubules (reviewed in [2, 3]).
Can cells divide without centrosome
In summary, it is now clear that mitotic spindles have a remarkable capacity to self-assemble and direct animal cell division without centrosomes.
What is the centrosome in mitosis
A centrosome is an organelle located near the nucleus in the cytoplasm that divides and migrates to opposite poles of the cell during mitosis and is involved in the formation of the mitotic spindle, assembly of microtubules, and regulation of cell cycle progression.



0 Comments